A San Bernardino plan to exit bankruptcy follows the path of the Vallejo and Stockton exit plans, cutting bond debt and retiree health care but not pensions. Then it veers off in a new direction: contracting for fire, waste management and other services.
The contract services are expected to reduce city pension costs. Other pension savings come from a sharp increase in employee payments toward pensions and from a payment of only 1 percent on a $50 million bond issued in 2005 to cover pensions costs.
Last week, a member of the city council had a question as a long-delayed “plan of adjustment” to exit the bankruptcy, declared in August 2012, was approved on a 6-to-1 vote, meeting a May 30 deadline imposed by a federal judge.
“The justification from what I’m understanding from the plan — the justification for contracting is more or less to save the city from the pension obligation. Is that correct?” said Councilman Henry Nickel.
One of the slides outlining the summary of the recovery plan said: “CalPERS costs continue to escalate, making in-house service provision for certain functions unsustainable.”
The city manager, Allen Parker, told Nickel “that’s part of it” but not the “entirety.”
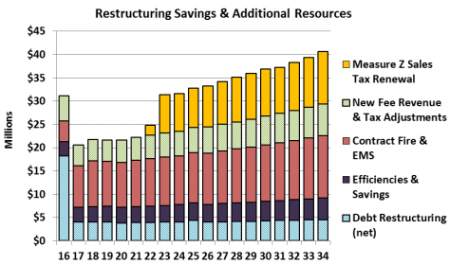
In addition to pension savings, he said, contracting with a private firm for refuse collection now handled through a special fund is expected to yield a “$5 million payment up front” into the deficit-ridden city general fund.
Parker said the California Public Employees Retirement System safety rate for firefighters is between 45 and 55 percent of base pay. “So if you have a fireman making say $100,000 a year, there is another $50,000 a year that goes to CalPERS,” he said.
An actuary estimated that contracting for fire services could save the city $2 million a year in pension costs, Parker said. The city expects total savings of $7 million or more a year, similar to a Santa Ana contract with the Orange County Fire Authority.
Unlike other unions, firefighters have not voluntarily agreed to help the struggling city by taking a 10 percent pay cut and foregoing merit increases. The cost of firefighter overtime has averaged $6.5 million in recent years.
After the court allowed the city to overturn a firefighter contract requiring “constant manning” last year, the city expected reduced staffing during off-hours. But overtime has not decreased, wiping out anticipated savings of $2.5 million this year.
Negotiations with the firefighters are difficult, Parker said, and their union has filed several lawsuits. He said the situation is “out of hand” and “can’t be contained,” part of the reason for the plan to contract for fire services.
The city expects fire service bids from San Bernardino County and others. A private firm, Centerra, has shown interest. Councilman Nickel said a legislator called about contracting with a private firm, suggesting “concern at the state level.”
Parker said a contract with a private firm would need a mutual aid agreement with neighboring government fire services. He said a San Manuel private fire service has been accepted by a fire chiefs association that manages the regional agreements.
Contracting for police services is not planned. Parker said the “one possible agency,” the San Bernardino County Sheriff‘s Department, made a $60 million proposal in 2012, reaffirmed last year, that would not yield city savings.
Fire and waste management are the biggest opportunities for savings and revenue among 15 options for contracting city services listed in the recovery plan summary. City employees are expected to be rehired by contractors.
Estimated annual savings are listed for contracting five other services: business licenses $650,000 to $900,000, fleet maintenance $400,000, soccer complex management $240,000 to $320,000, custodial $150,000, and graffiti abatement $132,600.
In the 1960s, San Bernardino was the “epitome of middle-class living,” said the plan summary, and then a “profound and continuous decline” turned it into the poorest California city of its size (214,000).
Median San Bernardino household income was at the California average in 1969, an inflation-adjusted $54,999, before steadily falling by 2013 to $38,385, well below the state average of $61,094.
Financial trouble began before the recession. A unique form of government created “crippling ambiguities” of authority among the city manager, mayor, council and elected city attorney, leaving no one clearly in charge as the city slowly sank.
When the reckoning finally came in 2012, San Bernardino faced an $18 million cash shortfall and an inability to make payroll. After an emergency bankruptcy filing, the city became the first to skip its annual payments to CalPERS.
Now the skipped payment of $14.5 million is being repaid over two fiscal years with equal installments of about $7.2 million. The recovery plan also said with no elaboration: “FY 2019-20: $400,000 annually in penalties and interest.”
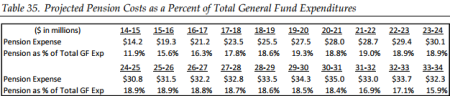
Replying to Nickel last week, the city manager explained why, if most employees are to be replaced by contract services, the plan does not propose to cut CalPERS debt. The city’s pensions have an “unfunded liability” of $285 million and are 74 percent funded.
Parker said the plan protects pension amounts already earned by city employees, even with a new employer, and like the Stockton and Vallejo plans reflects the view that pensions are needed to compete with other government employers in the job market.
“We naively thought we could negotiate more successfully, but that didn’t necessarily happen,” Parker said of mediation with CalPERS. An early plan called for a “fresh start” stretching out pension payments, yielding small savings in the first years.
And like Vallejo but not Stockton, which said from the outset it did not want to cut pensions, Parker said there was fear of a costly and lengthy legal battle with deep-pocketed CalPERS, possibly all the way to the U.S. Supreme Court.
One of the unique provisions in the San Bernardino city charter, which voters declined to overturn last year, bases police and firefighter pay on the average safety pay in 10 other cities, not labor bargaining.
Despite that link, police and firefighter compensation is said to be 8 to 10 percent below market because of low benefits. The bankrupt city stopped paying the employee CalPERS share and raised police and firefighters rates to 14 percent of pay.
Higher pension contributions from employees saved the city about $8 million last fiscal year, the plan said. Retiree health payments were reduced from a maximum of $450 per month to $112 per month, saving $213,750 last year.
“The filing of the plan is only the beginning of a long and very difficult process regarding confirmation and continued litigation with some of our creditors,” the city attorney, Gary Saenz, told the city council last week.
[divider] [/divider]